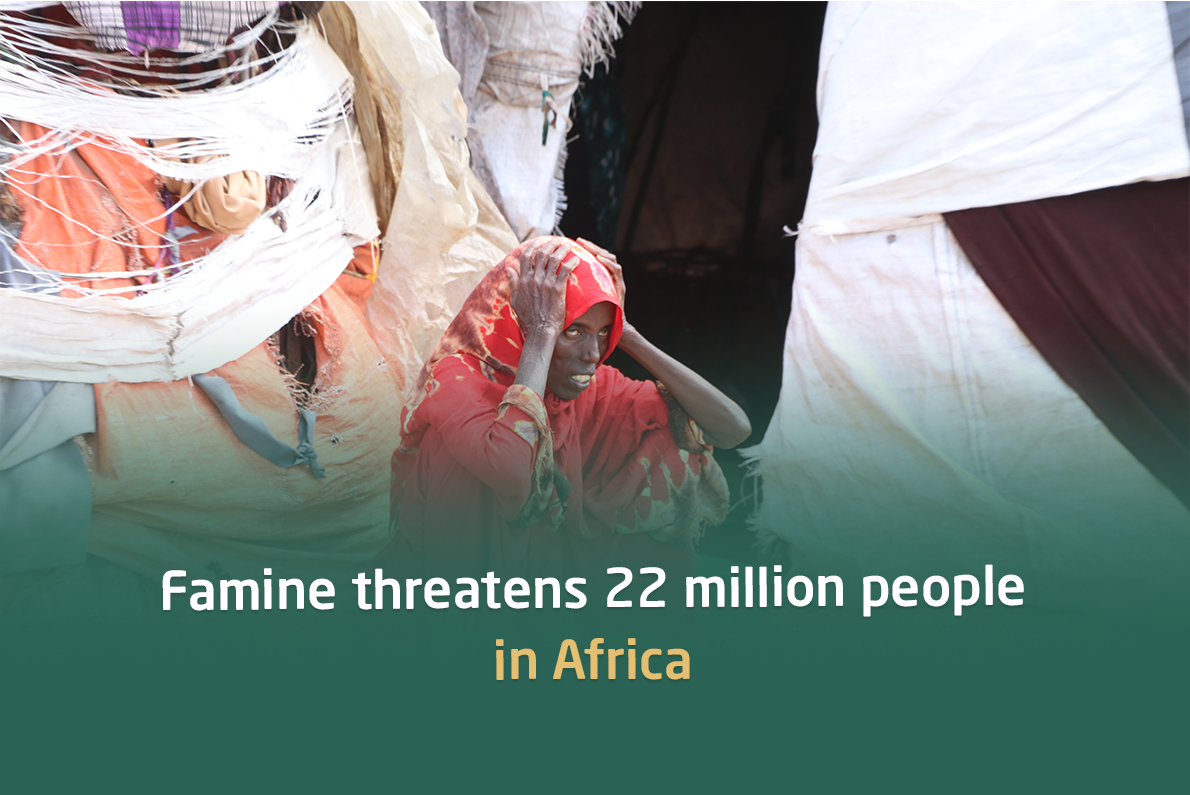
Famine threatens 22 one million people in Africa
Famine in Africa is a chronic and complex problem that causes millions of people to suffer. Recent reports indicate that about 22 million people are at risk of starvation on the African continent. To better understand this crisis, it is important to consider the multiple factors that contribute to the persistence of famine and identify sustainable solutions that can alleviate this crisis.
The root causes of famine in Africa a comprehensive analysis
Famine in Africa is a complex and multidimensional problem that requires a deep understanding of the root causes that exacerbate it. Here, we will review the historical, economic, environmental, social and political factors that contribute to the continuation of the famine crisis on the African continent, and explain the impact of each factor in an expanded form.
Historical factors
Colonization:
European colonization played a huge role in shaping the economic and social landscape of Africa. During the colonial period, Europeans reorganized local economies to serve their own needs, which negatively affected traditional farming systems. Vast tracts of agricultural land have been converted to grow cash crops such as cotton and coffee, rather than the staple food crops on which local communities depend. This transformation has led to the destruction of local agricultural systems and the reduction of agricultural diversity, making African communities more vulnerable to hunger.
Civil wars and conflicts:
Many African countries are experiencing constant armed conflicts and civil wars. These conflicts lead to the destruction of infrastructure, disruption of agricultural production, displacement of the population, undermining economic systems. Under conflicts, it becomes difficult to implement development projects and improve food security, which exacerbates the problem of hunger and famine.
Economic factors
Poverty:
Poverty is one of the most prominent economic factors contributing to the continuation of famine in Africa. Many Africans live below the poverty line, which limits their ability to buy or produce enough food to meet their daily needs. Poverty leads to a lack of access to basic resources such as water, agricultural land and modern agricultural technology, which hinders agricultural productivity and increases dependence on external food aid.
Dependence on foreign aid:
Many African countries rely heavily on foreign food aid to meet their needs. Although this assistance provides a temporary solution to the crisis, it may create a situation of dependence and unsustainability in the long term. Dependence on foreign aid prevents the development of sustainable local solutions to food security, and hinders the building of local capacities that can adapt to agricultural challenges.
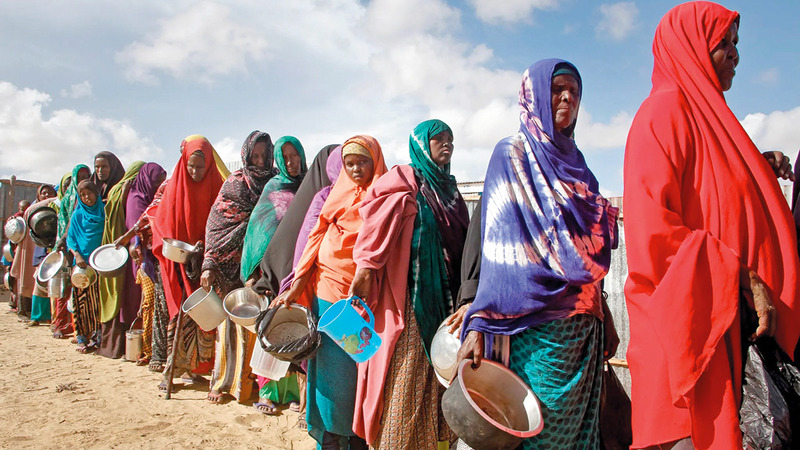

Environmental factors
Climate change:
Climate change is a major threat to agriculture in Africa. The continent is experiencing an increase in the frequency and severity of droughts and floods, which leads to a decrease in the productivity of agricultural crops and the destruction of Natural Resources. These harsh climatic conditions make it difficult for farmers to predict planting and harvesting seasons, which increases food instability.
Desertification and land degradation:
Desertification and land degradation are environmental problems that negatively affect soil fertility and crop productivity. Desertification reduces arable areas, while land degradation causes the soil to lose its essential nutrients. These challenges reduce the ability to produce food sustainably, and force the population to rely on food aid for survival.
Social and political factors
Corruption and mismanagement:
Corruption and mismanagement are structural problems that affect the distribution and efficient use of resources. In some African countries, resources are diverted away from vital sectors such as agriculture, health and education due to corruption. This leads to support and resources not being effectively directed to improving food security, and disrupts sustainable development efforts.
Rapid population growth:
Many African countries are experiencing rapid population growth, which increases the pressure on food resources and infrastructure. Without significant improvements in agricultural and economic production, it becomes difficult to meet the needs of a growing population. Population growth requires a constant increase in food production and the expansion of basic services, which is quite a challenge under current conditions.
Understanding the root causes of famine in Africa requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account historical, economic, environmental, social and political factors. Addressing this crisis requires the adoption of sustainable and comprehensive solutions that enhance the ability of societies to adapt and self-sufficiency. By improving agriculture, investing in infrastructure, fighting corruption, and promoting education and awareness, real progress can be made towards eradicating famine on the African continent.
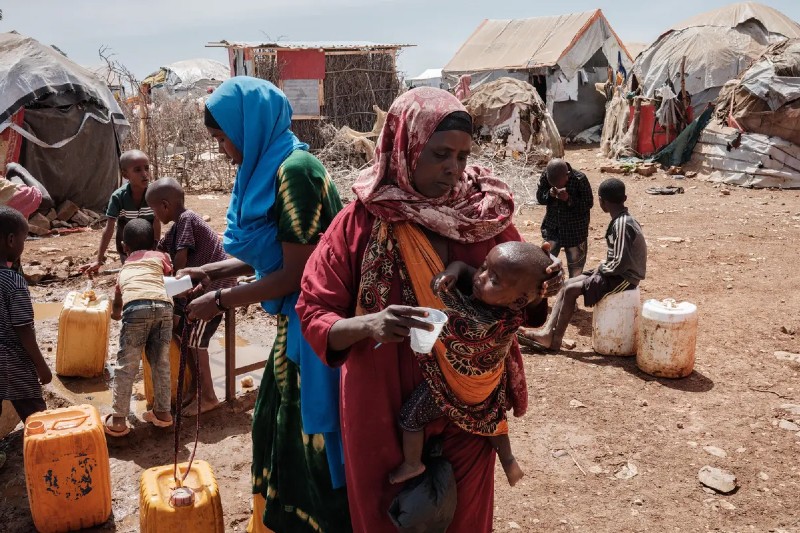

Sustainable solutions to famine in Africa
Famine in Africa is an ongoing and complex challenge that requires the adoption of comprehensive and sustainable strategies to address it. These solutions target the environmental, economic, social and political factors contributing to the aggravation of the crisis. Below is a detailed review of possible solutions:
Promoting sustainable agriculture
Technologies such as drip irrigation, vertical farming, organic farming can significantly improve the efficiency of agricultural production. Drip irrigation reduces water consumption and improves its access to plant roots, which increases agricultural productivity. Vertical farming and organic farming contribute to increasing food productivity while maintaining ecological balance. In addition, research and development in the areas of crop improvement and the development of new technologies to combat pests and climatic changes should be strengthened. These technologies help to cope with environmental challenges, improve crop quality and increase productivity.
Sustainable soil management includes practices such as crop rotation and conservation agriculture that preserve soil fertility and improve productivity. Crop rotation helps replenish nutrients in the soil, while conservation agriculture reduces soil erosion and preserves its structure. The development of rainwater harvesting systems and effective irrigation helps to cope with water scarcity in dry areas. These systems enable the collection and storage of water to be used for irrigation during dry periods, ensuring the availability of water for crops all year round.
Growing diverse crops, including native crops that are more resistant to drought and pests, can enhance food diversity and reduce the risk of agricultural failure. Diverse crops help improve food security by providing multiple sources of food, reducing dependence on a single crop. The cultivation of drought-and pest-resistant crops contributes to the sustainability of agricultural production and minimizes losses caused by harsh climatic conditions and agricultural diseases.
Investment in infrastructure
The construction of roads and bridges and the improvement of transport infrastructure ensure that agricultural products from farmers reach the markets quickly and efficiently, reducing food waste. Good roads facilitate the transportation of crops from production areas to local and international markets, which increases the opportunities for farmers to sell their products and improves their income. Well-developed transport networks also promote economic integration between rural and urban areas, promoting inclusive development.
The establishment of refrigerated storage facilities and insect-resistant facilities can help reduce crop losses after harvest. Good storage preserves the quality of food and reduces waste caused by spoilage and spoilage. The application of modern inventory management technologies ensures the preservation of food quality for longer periods, which increases the availability of food throughout the year and reduces price fluctuations.
The use of solar-based irrigation systems and smart irrigation technologies can increase the efficiency of water use. These systems rely on sustainable energy sources and technologies that allow precise control of the amount of water used, reducing waste and improving agricultural productivity. Encouraging the use of solar and wind energy in the operation of water pumps and irrigation systems enhances agricultural productivity and provides sustainable solutions to meet the energy needs of rural areas.
Improving governance
Promoting transparency and applying strict anti-corruption laws ensures the efficient use of resources to achieve agricultural development. Corruption reduces the effectiveness of development programs and disrupts the fair distribution of aid. The establishment of independent oversight bodies to monitor the distribution of aid and ensure its access to beneficiaries can improve resource management and enhance confidence in government and institutions.
Improving systems for collecting and analyzing data on agricultural production and food distribution can help in making informed decisions. Accurate data helps to understand the needs of different regions and accurately determine priorities. Enhancing transparency by sharing information with local communities and NGOs ensures better cooperation and effective results. Participating communities are better able to interact with development programs and provide feedback to improve performance.
Education and outreach
Implementing educational programs in schools and communities to sensitize people to the importance of food diversity and proper nutrition can improve public health and reduce malnutrition rates. Nutrition education helps individuals to choose healthy foods and prepare them in sustainable ways. Organizing awareness campaigns to raise awareness of the importance of healthy food and how to prepare it in sustainable ways can enhance good eating habits in communities.
Providing training courses to farmers on best agricultural practices, such as water management and the use of organic fertilizers, can improve agricultural productivity and promote environmental sustainability. Cooperation with universities and research institutions to provide practical and technological training to farmers that can help adopt modern technologies and improve their agricultural skills.
Encouraging the cultivation of local crops and protecting biodiversity contributes to increasing resistance to natural disasters and diseases. Biodiversity enhances the sustainability of agroecosystems and reduces the risks associated with growing a single crop. Educating local communities about the importance of preserving the environment and natural resources to ensure the sustainability of agricultural production can enhance environmental protection and improve the quality of life.
The role of AHAD in combating poverty and achieving sustainable development in Africa
AHAD works in the heart of the African continent, focusing its efforts especially in the countries of Central and West Africa with the aim of improving the quality of life of the poor and disadvantaged in those regions. The organization’s projects cover vital areas including health, education, water, and economic development. AHAD adopts strategies that leverage the skills and capabilities of local individuals, promote community participation and empower local people to achieve sustainable development.
AHAD seeks to achieve sustainable and positive impacts through all its projects, aiming to empower individuals and communities to become self-sufficient and contribute effectively to building a bright future for their future generations. Thanks to its continuous efforts, AHAD contributes to making a real and tangible difference in the lives of thousands of people, embodying its motto “because it deserves life” in every step it takes towards sustainable development.
You can visit the AHAD website to find out more about the projects it offers
ALSO READ
WHAT THE FOOD BASKET CONTAINS IN AHAD
Join us in our message